dtesselstrom
- 29
- 0
Homework Statement
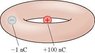
What is the net electric flux through the torus (i.e., doughnut shape) of the figure
Homework Equations
net flux= E*A I believe is needed
The Attempt at a Solution
I don't know how to do this problem at all. I feel like I don't have enough information to calculate the answer. Any advice as how to start this problem because I don't have the radius of the objects so how can I figure out the area.