- #1
neik
- 15
- 0
Does anyone know how to solve this?
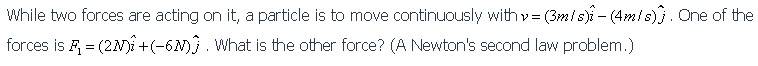
Newton's first law, also known as the law of inertia, states that an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will continue in motion with a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force.
Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass. In equation form, this is written as F=ma, where F is the net force, m is the mass, and a is the acceleration.
Newton's third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that when one object exerts a force on another object, the second object will exert an equal and opposite force back on the first object.
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is a measure of the force of gravity acting on an object. According to Newton's laws, an object's mass remains constant regardless of its location, while its weight can vary depending on the strength of gravity.
Objects in free fall are subject to the force of gravity, which is a constant acceleration. This means that according to Newton's second law, the force of gravity acting on the object will cause it to accelerate at a constant rate. Additionally, Newton's third law applies as the object exerts an equal and opposite force on the Earth as it falls.