seto6
- 248
- 0
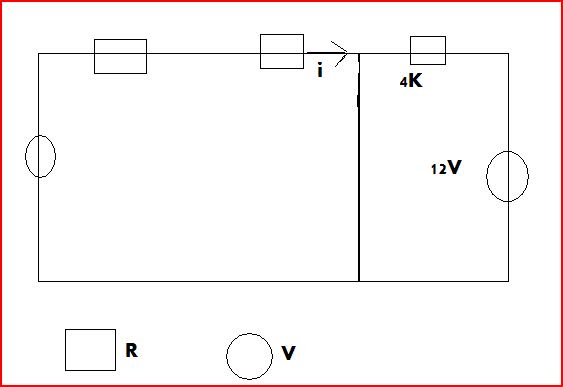
ok this is what i have, i want to know if the current would go through the 12V and 4k ohm resistor, since there is a short path (by making the inductor a short for time = infinity) would the current be lazy and take the path through the short or would it also go through the 12v and 4k ohm.