- #1
PetePetePete
- 8
- 1
I am struggling with a question in my coursework, and would appreciate some guidance.
The question is:
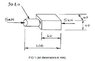
The component shown in Fig 1 is made from a material with the following properties and is subjected to a compressive force of 5kN.
Material Properties :
Young’s Modulus of Elasticity – 200 GNm-2
Modulus of Rigidity – 90 GNm-2
Poisons ratio – 0.32Calculate :
(a) The stress in :
(i) the circular section
(ii) the square section
(b) The strain in :
(i) The circular section
(ii) The square section
(c) The change in length of the component
(d) The change in diameter of the circular section
(Figure 1 is attached)
I have worked out question 1 i) and ii) to be 7.07Pa and 3.125Pa respectively, but I do not know where to begin with the rest of this question.
Thanks,
Pete
The question is:
The component shown in Fig 1 is made from a material with the following properties and is subjected to a compressive force of 5kN.
Material Properties :
Young’s Modulus of Elasticity – 200 GNm-2
Modulus of Rigidity – 90 GNm-2
Poisons ratio – 0.32Calculate :
(a) The stress in :
(i) the circular section
(ii) the square section
(b) The strain in :
(i) The circular section
(ii) The square section
(c) The change in length of the component
(d) The change in diameter of the circular section
(Figure 1 is attached)
I have worked out question 1 i) and ii) to be 7.07Pa and 3.125Pa respectively, but I do not know where to begin with the rest of this question.
Thanks,
Pete