Homework Help Overview
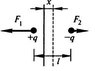
The discussion revolves around calculating the time period of small oscillations of a point dipole placed in an infinite flat layer with a specified volume charge density. The charge density varies with the position along the axis perpendicular to the plane, and participants are exploring the implications of this setup on the electric field and oscillation characteristics.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning, Problem interpretation, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss the application of different unit systems (CGS vs. SI) and how this affects their calculations. There are attempts to derive the electric field from the given charge density, with questions about constants of integration and the behavior of the electric field at specific points. Some participants express confusion about the dipole's position and its implications for the electric field.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with various interpretations being explored. Some participants have provided hints and suggestions for approaching the problem, including the use of Gauss's theorem. However, there is no explicit consensus on the correct approach or final expression for the electric field or oscillation period.
Contextual Notes
Participants note that the problem statement may lack sufficient information, particularly regarding the separation distance of the dipole charges, which is critical for determining the frequency of oscillations. There are also discussions about the implications of the charge density being zero at certain points and how this affects the electric field.