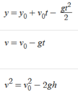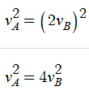Juliusz
- 13
- 3
Homework Statement
Ball A is dropped from rest from a building of height H exactly as ball B is thrown up vertically from the ground. When they collide A has twice the speed of B. If the collision occurs at height h, what is h/H?
Homework Equations
(I would type them out put I can't format them properly, sorry)
The Attempt at a Solution
I did everything as in the example, but then I got to the part where we compare the speeds. The formula (red arrow) show that at the time of impact, the speed of A is 4 times greater than speed of B. But in the problem, it states that the speed of A is only twice the speed of B. So my understanding is that there should be a 2 instead of a 4. Am I missing something?