You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
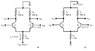
What is the difference in applying -ve voltage at emitter and +ve coll
- Thread starter dexterdev
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Difference Voltage
AI Thread Summary
The discussion centers on the impact of applying negative voltage at the emitter versus positive voltage at the collector in transistor circuits. It highlights that the power supply voltages influence the necessary input voltages, with specific examples showing how different negative supply levels affect transistor operation. The first circuit operates as a basic Emitter-Coupled Logic (ECL) unit, with defined input voltage ranges for logic states. The second circuit, while functionally similar, does not support the same input/output voltages as the first. Understanding these differences is crucial for designing effective transistor circuits.
Engineering news on Phys.org
vk6kro
Science Advisor
- 4,079
- 41
The power supply voltages also affect the necessary input voltages.
For example in the second diagram, the transistor with -1.3 volts on its base will be turned off if the negative supply line is grounded but it is conducting if this line is at -5.2 volts.
This is because the base is more positive than the negative supply line in the second case, but less positive in the first case.
NascentOxygen
Staff Emeritus
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 9,249
- 1,080
Over what range of input voltages will the arrangement in (a) function as an amplifier?dexterdev said:What is the difference in applying -ve voltage at emitter and +ve voltage at collector in attached circuit image? Really what I think is both circuits in thae image are identical. But then why -VEE?
-Devanand T
What about (b)?
dexterdev
- 194
- 1
the circuit in (a) is basic ECL unit, range of inputs is 2 logic states at input -1.7 V and -0.8 V.
I was asking that what difference (a) has with (b) in voltage supply applied in terms of polarity.
Last edited:
NascentOxygen
Staff Emeritus
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 9,249
- 1,080
(b) will function in the same manner, but not with the input/output voltages that cause (a) to work.dexterdev said:the circuit in (a) is basic ECL unit, range of inputs is 2 logic states at input -1.7 V and -0.8 V.
I was asking that what difference (a) has with (b) in voltage supply applied in terms of polarity.
I have recently moved into a new (rather ancient) house and had a few trips of my Residual Current breaker.
I dug out my old Socket tester which tell me the three pins are correct. But then the Red warning light tells me my socket(s) fail the loop test.
I never had this before but my last house had an overhead supply with no Earth from the company. The tester said "get this checked" and the man said the (high but not ridiculous) earth resistance was acceptable. I stuck a new copper earth...
Hi Guys
We are a bunch a mechanical engineers trying to build a simple electromagnet. Our design is based on a very similar magnet. However, our version is about 10 times less magnetic and we are wondering why. Our coil has exactly same length, same number of layers and turns.
What is possibly wrong? PIN and bracket are made of iron and are in electrical contact, exactly like the reference design.
Any help will be appreciated.
Thanks.
edit: even same wire diameter and coil was wounded by a...
Even as a kid, I saw beauty in old devices. That made me want to understand how they worked. I had lots of old things that I keep and now reviving. Old things need to work to see the beauty. Here's what I've done so far.
Two views of the gadgets shelves and my small work space:
Here's a close up look at the meters, gauges and other measuring things:
This is what I think of as surface-mount electrical components and wiring. The components are very old and shows how...
Similar threads
- Replies
- 12
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 10
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 68
- Views
- 6K
- Replies
- 35
- Views
- 5K
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 16
- Views
- 9K
- Replies
- 15
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 12
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 93
- Views
- 7K
Hot Threads
-
Spain’s power outage
- Started by Guineafowl
- Replies: 59
- Electrical Engineering
-
Using Latex Code for Circuit Diagrams
- Started by neilparker62
- Replies: 25
- Electrical Engineering
-
What is the difference between a switch leg and a hot leg?
- Started by sevensages
- Replies: 37
- Electrical Engineering
-
LTSpice DC - AC Inverter Schematic Help
- Started by NightStar
- Replies: 4
- Electrical Engineering
Recent Insights
-
Insights Quantum Entanglement is a Kinematic Fact, not a Dynamical Effect
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 11
- Quantum Physics
-
Insights What Exactly is Dirac’s Delta Function? - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 3
- General Math
-
Insights Relativator (Circular Slide-Rule): Simulated with Desmos - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 1
- Special and General Relativity
-
Insights Fixing Things Which Can Go Wrong With Complex Numbers
- Started by PAllen
- Replies: 7
- General Math
-
Insights Fermat's Last Theorem
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 105
- General Math
-
Insights Why Vector Spaces Explain The World: A Historical Perspective
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 0
- General Math