stunner5000pt
- 1,443
- 4
pleas help! electric field
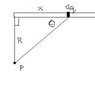
a semi infinite insulting rod carries a constant charge per unit length of lambda. SHow that he electric field at the point P makes an angle of 45 with the rod and that this result is independant of R
q = \lambda x
dq = \lambda dx
for the Y direction poiting downward
dE_{y} = \int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{1}{4 \pi \epsilon_{0}} \frac{\lambda dx}{R^2 + x^2} \sin{\theta}
\sin{\theta} = \frac{x}{R^2 + x^2}
dE_{y} = \int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{1}{4 \pi \epsilon_{0}} \frac{\lambda R dx}{(R^2 + x^2)^\frac{3}{2}}
dE_{y} = \frac{\lambda R}{4 \pi \epsilon_{0}} \int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{dx}{(R^2 + x^2)^\frac{3}{2}}
dE_{y} = \frac{\lambda R}{4 \pi \epsilon_{0}} [\frac{x}{R^2 \sqrt{R^2+x^2}}]_{0}^{\infty}
now I am not sure about this integral and whether or not it converges...
for the horizontal pointing left
\frac{\lambda R}{4 \pi \epsilon_{0}} \int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{xdx}{(R^2 + x^2)^\frac{3}{2}}
same problem here
please help!
a semi infinite insulting rod carries a constant charge per unit length of lambda. SHow that he electric field at the point P makes an angle of 45 with the rod and that this result is independant of R
q = \lambda x
dq = \lambda dx
for the Y direction poiting downward
dE_{y} = \int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{1}{4 \pi \epsilon_{0}} \frac{\lambda dx}{R^2 + x^2} \sin{\theta}
\sin{\theta} = \frac{x}{R^2 + x^2}
dE_{y} = \int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{1}{4 \pi \epsilon_{0}} \frac{\lambda R dx}{(R^2 + x^2)^\frac{3}{2}}
dE_{y} = \frac{\lambda R}{4 \pi \epsilon_{0}} \int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{dx}{(R^2 + x^2)^\frac{3}{2}}
dE_{y} = \frac{\lambda R}{4 \pi \epsilon_{0}} [\frac{x}{R^2 \sqrt{R^2+x^2}}]_{0}^{\infty}
now I am not sure about this integral and whether or not it converges...
for the horizontal pointing left
\frac{\lambda R}{4 \pi \epsilon_{0}} \int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{xdx}{(R^2 + x^2)^\frac{3}{2}}
same problem here
please help!
Attachments
Last edited: