Lnewqban
Homework Helper
Gold Member
- 4,155
- 2,367
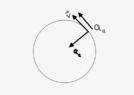
I see that applicable to D) only.haruspex said:We do not need to concern ourselves with forces here. It is purely a kinematic question. Somehow the acceleration is made to have this relationship to the velocity. We do not care how.
If the tennis ball is changing trajectory, forces and accelerations are acting upon it.
As I see it, for the angle between the constantly changing direction of the velocity and the acceleration vectors of the ball to be kept at a constant angle, the constant direction of the weight force disqualifies to be coplanar with the non-linear trajectory.