xtrubambinoxpr
- 86
- 0
Hello all! I hope I am posting this in the right place.
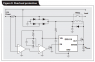
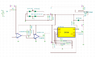
I am looking for some help on the following circuit. Basically I am doing a relay application using one of TI's chips. Below is the reference design from an app note along with my actual circuit modeled in TINA. The main function is that using the comparators it will toggle the relay when an overload is detected. This is my first real circuit design application so any assistance with it I would greatly appreciate it. I am looking for tips and a walk through so I can arrive to the solution rather than being given one. Any other questions please ask!
Problems:
I am looking for some help on the following circuit. Basically I am doing a relay application using one of TI's chips. Below is the reference design from an app note along with my actual circuit modeled in TINA. The main function is that using the comparators it will toggle the relay when an overload is detected. This is my first real circuit design application so any assistance with it I would greatly appreciate it. I am looking for tips and a walk through so I can arrive to the solution rather than being given one. Any other questions please ask!
Problems:
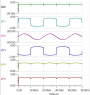
- There is a supply of 110 VAC being provided through J1. The transient response shows that the voltage at VF4/VF5 does not exceed 2V. Why? my thoughts are that it is not being rectified correctly and/or there is a mistake in my design with the cap/resistor at the output.
- How can I verify a rectified Voltage at the output?
- Can the input into the comparator be AC? It seems like its just going to keep toggling and my thoughts are that everything should be rectified and supplied to the system as DC.