cupid.callin
- 1,130
- 1
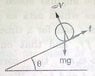
Homework Statement
The Attempt at a Solution
The sphere is rolling without sipping, so the lowermost point has 0 velocity ... so why would there be any friction?
I know that if there will be no friction .. sphere will just slide down and not roll but still as i said ... why will there be any friction?