- #1
Ben_Walker1978
- 113
- 6
- Homework Statement
- steady flow energy equation
- Relevant Equations
- First law
I am looking for help on the following:
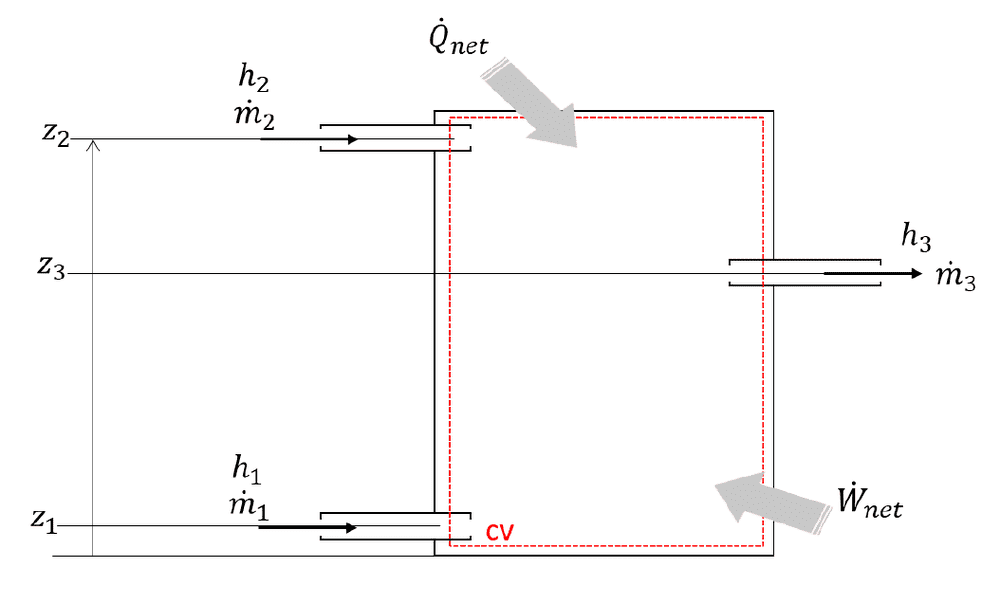
a) Given the system shown in the figure below, derive the steady flow energy equation from first principle.
b) Again using first principles, show how the energy equation would change for the case when the system is unsteady.
I am trying to learn this for upcoming exams.
But i can find nowhere on line which breaks down this sort of question. Which means i can't understand how to complete these sort of questions.
Can anyone help me complete this question please? So i can get an understanding of these types of questions.
Thanks
a) Given the system shown in the figure below, derive the steady flow energy equation from first principle.
b) Again using first principles, show how the energy equation would change for the case when the system is unsteady.
I am trying to learn this for upcoming exams.
But i can find nowhere on line which breaks down this sort of question. Which means i can't understand how to complete these sort of questions.
Can anyone help me complete this question please? So i can get an understanding of these types of questions.
Thanks