Abdulwahab Hajar
- 56
- 2
Homework Statement
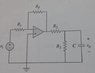
In the figure given what is the Thevenin resistance between the nodes of the capacitor??
Homework Equations
The Thevenin resistance is the open node resistance between two points.
The Attempt at a Solution
The way I see it, R2, Rf and R1 are in series and that combination is in parallel with R3...
However the book says that Rf, and R1 don't count because the output resistance of the op-amp is 0 since it's ideal...
Is that correct?? and what is output resistance to begin with?
Thank you