Time Definition and 997 Threads
-

MATLAB Change the value of a variable at each time step in matlab?
hi guys I am trying to implement the a second order differential equation tat contains a time dependent term, the equation looks something like r'' = -\mu/r^3+(g/g^3-m/m^3) the idea is that i want to calculate 'r' the position vector of a point, that is dependent on vectors g and m, I tired to...- patric44
- Thread
- Change Matlab Ode45 Time Value Variable
- Replies: 8
- Forum: MATLAB, Maple, Mathematica, LaTeX
-

Undergrad Negative Distance Metric: Elapsed Time & Space-Time Interval
DISTANCE METRIC, 2D: $$d = \sqrt{x^2 + y^2}$$ DISTANCE METRIC, 3D: $$d = \sqrt{x^2 + y^2 + z^2}$$ DISTANCE METRIC, 4D: $$d = \sqrt{x^2 + y^2 + z^2 - ct^2}$$ You SUBTRACT elapsed time from the spatial distance. Yes, elapsed time is called "imaginary distance," and vice versa. However...- Paige_Turner
- Thread
- Negative Time
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Time Dependence of Wave Function
I started out by finding the w (omega) value for all of the three states but I'm not sure where to go from there.- sarahjohn
- Thread
- Function Time Time dependence Wave Wave function
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

High School Is time a consequence of 2nd law of thermodynamics?
I have heard from a knowledgeable physics proffessor, time exists independently and it is not a consequence of arrow of time. Could some body explain this?- Ebi Rogha
- Thread
- 2nd law Arrow of time Entropy Law Thermodynamics Time
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-

High School Time Dilation: Does Observer See Your Time Speed Up?
If time slows down for an observer traveling at some speed relative to your proper time, shouldn't the traveling observer also see your time slow down relative to his proper time? Or does the observer see your time speed up relative to his proper time. Also, is dilation exactly the same in...- AdvaitDhingra
- Thread
- Dilation Time Time dilation
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Undergrad Universe re-collapse and time reversal
If the universe were to re-collapse, the Hubble constant would increase over time. Since the age of the universe is the inverse of the Hubble constant, the age of the universe will decrease. Does that mean time reversal? -

Undergrad What is the confusion surrounding time as a coordinate in general relativity?
We study metrics, in them, we take time as a coordinate. I mean to say that if time is a coordinate then in normal mathematical language, we can have negative coordinate values as well. This confuses me a lot as I want to see and understand the concept from the true physicist's perspective...- AHSAN MUJTABA
- Thread
- General General relativity Relativity Time
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
Undergrad Calculating Time Elapsed in Rocket Collision
Consider an observer on Earth (Neglect any effect of gravity). Call him A. Let 2 rockets be moving in opposite direction along x-axis (x-axis coincides with the x-axis of A) with uniform velocities. Call them B and C. At t=0, in A's frame, the rockets are separated by length ##l## . Let ##V_a##...- Abhishek11235
- Thread
- Collision Rocket Special relativity Time
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
What is the Difference Between 12:00 AM and 12:00 PM?
Summary:: what do 12:00 AM and 12:00 PM really mean. How do you say the time at at noon. is noon 12:00 AM or 12:00 PM? 12:00 AM means 12 hours before meridian or before noon so 12:00 AM should mean 12 hours before noon or midnight. 12:00 PM means 12 hours past meridian or 12 hours...- arydberg
- Thread
- Time
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Art, Music, History, and Linguistics
-

High School Will there be a time when drawings stop being useful in mathematics?
I mean, as a simple example, vector analysis involves the study of higher-dimensional objects in Euclidean space, objects that are downright impossible to visualize using simply pencil and paper. When my professor taught it, he often explained the topics using analogies that tied into vector...- Eclair_de_XII
- Thread
- Mathematics Time
- Replies: 5
- Forum: General Math
-
S
High School Time Dilation Effect: Corrections to Clocks on ISS
Hello All The Hafele-Keating experiment in 1971 confirmed measurable time dilation effects on atomic clocks flown around the Earth on aircraft. Presumably clocks aboard the International Space Station suffer worse time dilation because of their greater speed in orbit. How often are corrections...- saddlestone-man
- Thread
- Clocks Dilation Iss Time Time dilation
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
N
Write a Linear Equation for the Value of this Printer Over Time
Write a linear equation. A school district purchases a high-volume printer, copier, and scanner for $24,000. After 10 years, the equipment will have to be replaced. Its value at that time is expected to be $2000. Write a linear equation giving the value V of the equipment during the 10 years it...- nycmathguy
- Thread
- Linear Linear equation Time Value
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Precalculus Mathematics Homework Help
-

High School What Is the Proper Time of the CMB and Its Implications?
Did some searches through these forums but didn't find this exact question. I'm sure it's already been asked, but I just missed it, my apologies. Please link. I’ll try and ask this question in 3 different ways, and maybe the idea behind it will become apparent. I know that semantics can really...- D.S.Beyer
- Thread
- Cmb Proper time Time
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
U
Graduate A question on proper time in special relativity
Homework Statement:: This isn't a homework but more of a conceptual question. Relevant Equations:: Proper time, ##\tau## Simply put, the proper time between two events as observed in an unprimed frame is calculated along the timelike worldline between the two events. This implies that the...- user1139
- Thread
- Proper time Relativity Special relativity Time
- Replies: 58
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
V
High School Combinations of 6 taken 4 at a time
the calculation 6C4 shows 15 but what if all sets are to be distinct? meaning 1,2,3,4 is the same as 4,3,2,1. I made a tree diagram and i get 10... assuming i did that correctly...?- Vector1962
- Thread
- Combinations Time
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Set Theory, Logic, Probability, Statistics
-

Rotating radar time domain data
I want to simulate the time domain data for a rotating radar. I assume that the space around the radar is filled up with a very big extended object and it moves with a constant speed in one direction. Picture attached.I don't take range information here. I am only concerned about the velocity as...- tworitdash
- Thread
- Data Domain Radar Rotating Time Time domain
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-

Graduate Kerr Metric Time Dilation Formula: Deriving Absolute Form
Just as the time dilation formula for the Schwarzschild metric in terms of the position ##r## away from center of mass for a gravitational body and the Schwarzschild radius ##r_s = {2GM}/{c^2}## is given by $$ \tau = t \sqrt{1 - \frac{r_s}{r} } $$ so I'd like to know the corresponding...- Dukon
- Thread
- Dilation Formula Kerr Kerr metric Metric Time Time dilation
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
G
High School Can there be time without mass?
According to Relativity, any object traveling at c will not experience time, because of time dilatation. It will seem to the object that it has traveled instantly while ages may pass outside. Further, an object without rest mass will always travel at c. Therefore, if there were no objects with a...- guptasuneet
- Thread
- Mass Time
- Replies: 64
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Undergrad Does Time Slow Down in a Deep Osmium Room?
So my idea is: Let's say you are in a room, that is 10km in the ground (so its closer to the center of gravity of earth) and made of Osmium. Could it be that the room, because of its mass, actually bends the space time with the Earth's help more so time could be running slower for you? If it is...- alpha_michi
- Thread
- Material Time
- Replies: 31
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
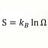
High School Time like spacetime interval, proper time, and time dilation
Since the time like spacetime interval is equal to proper time for stationary or traveling observers, then it seems time dilation (proper time) seen with traveling clock is necessarily frame invariant. Then the so called time between ticks of both identical clocks, with stationary and traveling...- Point Conception
- Thread
- Dilation Interval Proper time Spacetime Spacetime interval Time Time dilation
- Replies: 37
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Graduate Time of Impact of Gas Molecules on the Inner Wall of a Pressure Vessel
In derivation of relation for pressure of Gas ,(see pic below) the time for rate of change of momentum of molecules should be the time for which the wall of the vessel and the molecules kept interacting with each other, not the time between successive collisions. As circumscribed below, my...- Zahid Iftikhar
- Thread
- Gas Impact Molecules Pressure Pressure vessel Time Vessel Wall
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Mechanics
-
A
High School Time travel in the quantum world
hi users, I'm a new member of the forum. My question is about time travel in the quantum world. I am aware of the enormous limitations, but my topic is about individual particles and their ability to travel through time, is that possible for them? My question comes from a speech by an important...- Arceus
- Thread
- Quantum Time Time travel Travel
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
J
Programs Is doing a PhD in Engineering Part Time in 8 Years Possible?
Is it possible for me to get a PhD in electrical engineering while going part time, one class at a time? The college I'm thinking of going to has a 8 year time limit for PhDs before credits expire. 8 years seems like a long time. This would allow for 16 different classes, not sure if summer term...- JohnSmith0909
- Thread
- Engineering Part time Phd Time Years
- Replies: 19
- Forum: STEM Academic Advising
-
C
Undergrad Rate of Time/Mass: Is There a Constant?
Is there a constant for the rate at which time slows relative to the amount of mass? If so would there be a base measure eg time being present with 0 mass- CuriAus
- Thread
- Mass Relative Time
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
Thermal time scale in tubular flow reactors
So if I have a tubular reactor for nanoparticle synthesis (PTFE tubes ID:2mm). The tubes are heated in a furnace. liquid Reagents at room temperature are pumped by a syringe pump and directed toward the furnace. The reagents decompose to form nanoparticles once they reach the steady-state...- MSM
- Thread
- Flow Scale Thermal Time
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Materials and Chemical Engineering
-
T
Graduate Photon self-energy in the finite temperature field theory (real -time)
- Tian
- Thread
- Field Field theory Finite Photon Temperature Theory Time
- Replies: 4
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
G
Area Under Frequency versus Time Curve meaning?
Hello: Let's say you have a string and get data by changing the frequency a transverse wave in the string to get different standing modes. You measure the wavelength of each mode for each frequency. That is, the data you get are frequency and wavelength. Now, you are trying to find the...- GregB777
- Thread
- Area Curve Frequency Time
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Graduate How to estimate the interaction time of Raman scattering?
Maybe we could use (1) uncertainty principle $\Delta E \Delta t = \hbar$ and get $\Delta E$ from the spetrum. Or (2) forced vibration model, then get the damping factor $\gamma$, and get $Delta t = frac{1}{\gamma}$ -
N
MHB Which procedure takes the minimum time to solve modulus functions?
1) -|2x-3|+|5-x|+|x-10|=|3-x| 2) |2x-3|-|5-x|-|x-10|-|3-x|=28 3) -|2x-3|+|5-x|+|x-10|≥|3-x| How can we solve these problems? The method I know is to plug in the critical values to see which modulus becomes positive and which one becomes negative. Then find out the values of x for which the...- Nousher Ahmed
- Thread
- Functions Minimum Modulus Procedure Time
- Replies: 5
- Forum: General Math
-

Studying Help please -- Regarding good use of time during days off from college
My country has been hard hit by second wave of covid, so bad that the colleges that were conducting classes online had to be paused for two weeks. So since i have time, i am thinking of using it properly. I was wondering should i pursue how to proof in maths since i have linear algebra in my...- Carolus_Rex
- Thread
- College Need advice Time
- Replies: 6
- Forum: STEM Academic Advising
-
R
Earth's rotation slows down slightly over time -- How much energy is lost?
Inertia I = 2/5 mr² m=5.98* 10^24 kg. r=6.38* 10^6 kg. I= 9,736 * 10^37 kg. Earth rotation is V= (2 * pi* R)/T = (2*pi*6.38*10^6m)/(24*3600s)=463 m/s angular velocity w= V/r =463m/s/(6.38*10^6m)=7.27*10^-5 rad/s Enerrgy, E= 0.5* I*w²=2.57*10^29 j I get the...- robax25
- Thread
- Energy Lost Rotation Time
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Graduate Time Average Value of Pendulum String Tension
Another member and I, in private conversations, have been discussing the time average tension in a pendulum string. He has done a numerical analysis of the problem, and his calculations indicate that the time average tension is less than mg. I have analyzed the problem analytically by...- Chestermiller
- Thread
- Average Average value Pendulum String Tension Time Value
- Replies: 34
- Forum: Mechanics
-
R
Undergrad Length contraction and time dilation
A long time ago, I was very impressed by a lecture on elementary special relativity which showed in simple math how the correct conclusion to the null results of the Michelson-Morley experiment were obtained by concluding a constant c but then adding a length contraction and time dilation. I...- rasp
- Thread
- Contraction Dilation Length Length contraction Time Time dilation
- Replies: 36
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
H
Undergrad Time Reversal Breaking in Classical Systems
I am looking for an example of a classical system without time reversal symmetry. I would appreciate any help. -

Comp Sci Linear regression doubling time
y=mx+c by z=log y axis m=9-2.5 / 35 = 13/70 z=13/70 * (t-1983) + 2.5 log y = 13/70 * (t-1983) + 2.5 # doubling time: t1=y1, t2=y2=2y1 log y1 = 13/70 * (t1-1983) + 2.5 ---{1} log (2*y1) = 13/70 * (t2-1983) + 2.5 ---{2} {2}-{1}: log2=13/70 * [(t2)-(t1)] [(t2)-(t1)] = log2/(13/70) # for log...- yecko
- Thread
- Linear Linear regression Regression Time
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-

Undergrad Time-Dependent Lagrangian Leads to Time Dilation?
This is just something unexpected that I noticed recently, and I hadn't heard anyone mention it before. The relativistic Lagrangian for a particle moving under a scalar potential ##\Phi## is this: ##L = \frac{1}{2} m g_{\mu \nu} \dfrac{dx^\mu}{d\tau} \dfrac{dx^\nu}{d\tau} - \Phi## This leads...- stevendaryl
- Thread
- Dilation Lagrangian Time Time dilation
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
Riemann Sum to find the time to fill a container
(a) I imagine there are several rectangles to represent the area under graph of p vs t then I try to make equation for the total area. Since the question asks about time when the container holds 22 fewer liters than it does at time t = 9, I think the total area of rectangles starting from t = b...- songoku
- Thread
- Container Riemann Riemann sum Sum Time
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
J
Undergrad Is time really moving backwards?
I don't have much knowledge on general and special relativity except what I watch on youtube and read, btw. Edit: In addition, is traveling through a geodesic in spacetime relativistic between the object and spacetime itself? In other words, if I was traveling through a geodesic deep in space...- Joe30174
- Thread
- Time
- Replies: 155
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
N
What is the intersection point of two objects on a position vs time graph?
The graph: 1) $$v_1 = \frac{\Delta{x}}{t} = \frac{5 - 3}{3} = \frac{2}{3}$$ $$2 = \frac{\Delta{x}}{t} = \frac{4 - 0}{5 - 1} = 1$$ $$\frac{v_2}{v_1} = \frac{1}{2/3} = \frac{3}{2} = 1.5$$ 2)Points of intersection of the lines with the x-axis: ##I## (0; 3) and ##II## (0; -1), thus $$\frac{2}{3}t...- nmnna
- Thread
- Graph Graphs Position Time
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Finding lower and upper limit for time related to roller coaster
height from ground speed 100 40 80 48 60 60 40 72 20 80 I tried to plot the points (speed on x-axis and height on y axis) and I got more or less like a straight line but I am not sure whether the graph would help to calculate the upper and lower limit of the time. I also tried to...- songoku
- Thread
- Limit Roller Roller coaster Time
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

Undergrad Find time from distance-speed graph
In audio application i can automate playrate envelope (playhead speed) 1 = original speed, 2 = 2 x original speed, 3 = 3 x original speed etc.. Now i need to calculate time it takes for playhead to travel each section its easy to calculate time for section 1, where speed is constant time =...- Metaphysics
- Thread
- Graph Time
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Mechanics
-

Time period of 2 disks connected by a spring
My attempt at solving case B I've attached my attempt at case B above. What problem I'm facing is that after writing equation of angular SHM, I'm getting angular acceleration proportional to cube of angular displacement, which doesn't reduce to SHM. So how to find time period for this...- Vivek33010
- Thread
- Period Phy homework Spring Time Time period Torque and rotation
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
I
Find the time required for the current to grow to 2.5A....
what is the equation on finding the ''The time required for the current to grow to ...Amps'' i was asked to find The time required for the current to grow to 2.5Amps ,and i found out that its some where around 174.38ms, using Ltspice, but i want to find it out by calculating it out.- IronaSona
- Thread
- Current Time
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Undergrad Hyperbolic Time Chamber: Is Time Dilation Theoretically Possible?
Has anyone ever watched dragon ball Z before? In this TV show, there is something called the hyperbolic time chamber. 1 day on Earth is equivalent to 1 Year in the time chamber. In other words, if you stayed in the chamber for a full 24hours than exactly 1 year would have passed when you left...- Nick tringali
- Thread
- Chamber Dilation Hyperbolic Time Time dilation
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
C
High School Measuring Time: Identifying Slower Clock w/ Two Identical Clocks
If we have two clocks, A and B, that are identical, and if one is moving with respect to the other one, we know that they must run at different speeds. (Right?) One must run slower than the other. But we cannot tell which of the two clocks is the "moving" clock. So, how do we determine which...- crastinus
- Thread
- Measuring Time
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Mechanical device trigger with variable time delay (100-500ms)
This device, if it or something similar exists at all, needs to be completely mechanical without ANY electricity and be really precise and strong (to last a long time). Press a button in order to trigger the start of the delay time. It must start only when the button is fully pressed down (or...- tommy7
- Thread
- Delay Device Mechanical Time Time delay Variable
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-

How Long Does It Take for a Mass to Freeze or Melt?
Hello. We all know ##Q = mc\delta t##, but is there an equation which describes the time it takes for a mass to freeze/melt given a certain specific heat capacity? This way you could for example quantify how long it takes room temperature to freeze in a freezer (or any element).- Mayhem
- Thread
- Time
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
V
Determine time after which 4 persons meet in given scenario
The point of confusion is deciding the direction each persons sets out in i.e. velocity direction of each person. Knowing this will probably help in getting the solution. At t=0, I can say that velocity of each person is as shown in diagram below.- vcsharp2003
- Thread
- Kinematics Relative velocity Time Velocity
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

High School Is Proper Time Only Perceived by External Observers?
I am confused about the notion of proper time because it is defined as one's own time measured by one's own clock, but any given person is in all circumstances naturally at rest with respect to himself and therefore his "own proper time" is the coordinate t; am I wrong? So contrary to this...- Kairos
- Thread
- Proper time Time
- Replies: 32
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

High School Time Dilation Question: Two Men's Watches Differ after Space Travel
Sometime in the future two men meet at a space port and they synchronize watches, one boards a spacecraft and goes on a round trip around the solar system, when he returns the two men compare wristwatches to find they have different times. Q. Do the two men still exist at the same time or not?- Julius Ceasar
- Thread
- Dilation Time Time dilation
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Special and General Relativity